Check Number 3 Vocabulary
This is my vocabulary and examples for the third live review.
Vocabulary and Examples
- Binary Numbers: a numbering scheme in which there are only two possible values for each digit – 0 or 1 – and is the basis for all binary code used in computing systems
- Hexadecimal: a numbering system with base 16
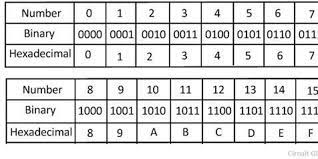
-
Bits: the smallest unit of data that a computer can process and store
- ex: 1 or 0 (one number in binary is a bit)
-
Bytes: a unit of data that is eight binary digits long
- ex: 10010110
-
Nibble: four consecutive binary digits or half of an 8-bit byte
- ex: 0101
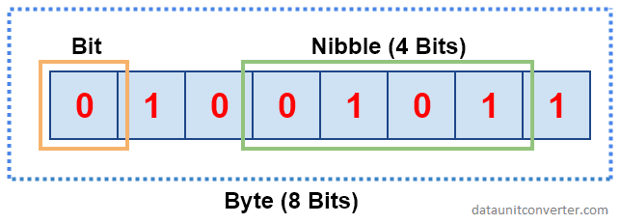
-
Unsigned Integer: integers but have the property that they don’t have a + or - sign associated with them
- ex: 2, 3, 6, 1000
-
Signed Integer: integers that have a + or - sign associated with them
- ex: -2, +3,000, -1
-
Floating Point: a positive or negative whole number with a decimal point
- ex: 3.25, 5.1, 67.627
- Binary Data Abstractions:
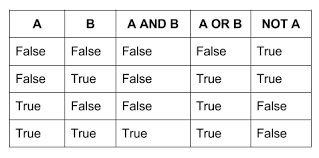
- Boolean: a logical data type that can have only the values true or false
- ASCII: (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) a standard code for characters stored in a computer or to be transmitted between computers
- Unicode: a universal character encoding standard
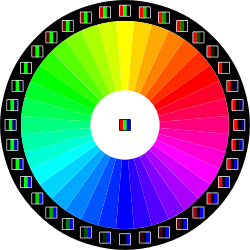
- RGB: a system for representing the colors to be used on a computer display
-
Data Compression: a reduction in the number of bits needed to represent data
- Lossy: data encoding and compression technique that deliberately discards some data in the compression process
- Lossless: restores and rebuilds file data in its original form after the file is decompressed
